Functioning Of The Kidneys: Their Anatomy And Functions
The kidneys are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure and for the functioning of vitamin D, among other functions.
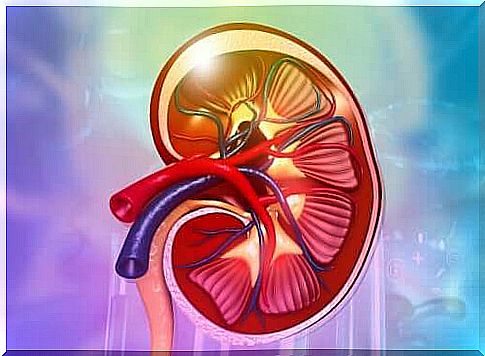
We are interested here in the functioning of the kidneys, complex organs responsible for eliminating via urine the substances from our body that represent waste. We have two kidneys that are shaped like a bean. They are found in the posterior part of the abdomen near the spine and under the ribs.
They are essential organs: without them, there is no possible life. However, thanks to technological advances, there are now techniques to replace these organs: dialysis and transplantation.
In addition to producing urine, the kidneys are involved in many other processes, such as regulating blood pressure. In this article, we tell you all about the function, anatomy and main characteristics of the kidneys.
The anatomy of the kidneys
As discussed earlier, the kidneys are shaped like a bean with one concave curve and another convex. From the side of the concave curve, enters the renal artery which carries blood with the body’s wastes which go to the kidneys. The renal vein and ureter also enter this concave curve.
The kidney is mainly made up of two parts: the cortex and the medulla. The cortex is the outermost part and the one that receives the most blood. It is mainly responsible for filtration and reabsorption. It also contains all the glomeruli that we will define later in this article.
The renal medulla is formed by a series of structures responsible for carrying urine to the ureter. The ureter is a conduit that travels downward and leads to the bladder where urine is stored and then eliminated.
The functional units of the kidneys are the nephrones. It is in the nephron that the filtration of blood and the creation of urine takes place. There are approximately 800,000 nephrons in each kidney.
The structure of nephrons is very complex. Roughly speaking, they are formed by a series of cell structures and membranes that allow blood to pass and be filtered. They are, moreover, responsible for secreting certain substances and reabsorbing others, such as potassium.
How the kidneys work: what are the kidneys for?
As discussed at the beginning of this article, the main function of the kidneys is to eliminate substances that represent waste through urine. But that is not their only function. These organs also play an important role in the secretion of certain hormones and substances.
First of all, it should be emphasized that the kidneys allow vitamin D to take its active form. This vitamin is essential for the metabolism of calcium.
The kidneys also produce erythropoietin, a substance responsible for stimulating the synthesis of red blood cells in our body.
Finally, the kidneys play a fundamental role in certain processes that allow homeostasis in our body. Homeostasis is a process that allows us to maintain internal balance despite changing external conditions.
For example, the kidneys regulate blood pressure and the pH of the blood. They also control plasma volume by altering the concentration of urine and they can prevent water loss in a situation of dehydration.
How do the kidneys filter the blood?
Blood arrives to the nephrons via the renal artery, where the latter branches into other smaller arteries that form the glomerulus. The glomerulus allows small molecules, fluids and toxins to pass to the tubules.
In addition, the glomerulus has a set of tubes in which a large part of the filtered water and certain substances that the body needs are reabsorbed. It can, for example, reabsorb molecules of sodium and potassium.
What should we remember about the functioning of the kidneys?
The kidneys are complex organs that, in addition to producing urine, perform many other vital functions. These functions include the synthesis of erythropoietin and the control of blood pressure.