Seborrheic Dermatitis: Symptoms And Treatment
Seborrheic dermatitis can affect both adults and infants. In general, it appears at stages of life when there is more intense sebaceous activity.
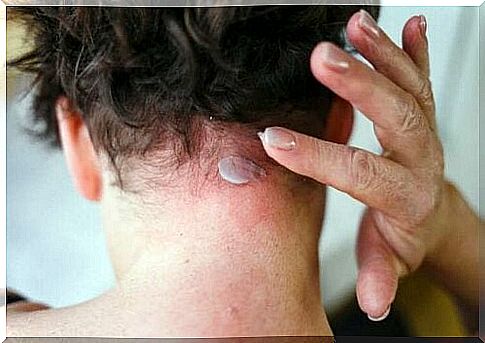
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition. It is a type of eczema that is not triggered by external factors. It mainly affects the scalp, although it can also be found on other areas such as the face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids and chest.
Seborrheic dermatitis can present in both adults and infants. In general, it appears at stages of life when there is more intense sebaceous activity, linked to greater hormonal stimulation.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is currently unknown. Nevertheless, its appearance can be linked to the malassezia fungus which is found in the sebaceous secretion of the skin. Another of the causes of seborrheic dermatitis can be an irregular response of the immune system.
There are a number of factors that can increase your risk of getting seborrheic dermatitis, such as having neurological and psychiatric conditions. Having a weak immune system also increases this risk, as does that of people who have organ transplants and people with HIV.
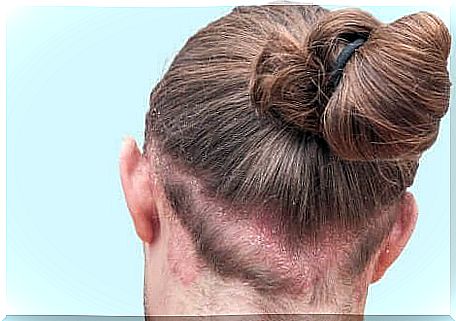
What are its symptoms?
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include: dandruff, lesions on the skin, itching, and mild erythema. Usually the scalp is always affected, so it often has scales.
Peeling of the eyebrows, eyelashes, beard hair and mustache is also common, as well as reddening and scaling of the nasolabial fold and the back of the ears.
In some patients, the eyelids become inflamed and small scabs form on their edges. In the trunk, seborrheic dermatitis usually manifests as rounded erythematous-squamous patches. The plaques are sometimes covered with very sticky scales, which look like lesions from psoriasis.
Diagnostic
Diagnosis is clinical, due to the appearance and location of the skin lesions. The patches with oily scales are particularly characteristic on the scalp.
Erythematosquamous lesions are also found in the scalp insertion areas, retroauricular folds, nasolabial folds or eyelashes. In babies, the characteristic lesion is the “cradle cap”.
A differential diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis should be made from other diseases that present with similar symptoms, such as:
- Psoriasis: It also causes dandruff and reddening of the skin with the presence of scales. These are more numerous and silvery white in color.
- Atopic dermatitis: This skin condition causes itching and inflammation on the skin of the folds of the elbows, the posterior part of the knees, and the front part of the neck.
- Tinea versicolor: This rash appears on the trunk but is usually not red like the patches of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Rosacea: in general, it occurs on the face and generates little dander.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
There are a whole series of general hygiene measures, such as avoiding showers with very hot water, environments with heating or air conditioning on, or situations of great emotional stress. For daily hygiene, neutral moisturizing soaps and moisturizing creams or lotions, non-greasy, should be used.
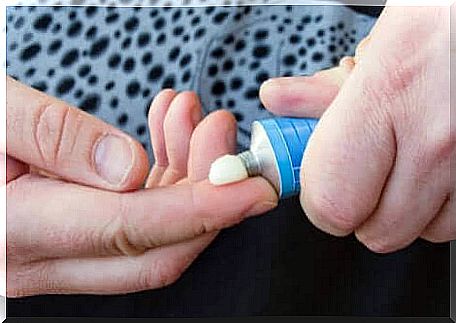
Anti-inflammatory
Corticosteroids like hydrocortisone, fluocinolone, and clobetasol are applied to the scalp or other affected area. They are used in the form of creams, shampoos or ointments.
They are effective and easy to use, but should be applied with caution. If used for too long without rest, they can cause side effects, such as thinning of the skin or the appearance of spots.
Creams or lotions that contain calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be effective and have fewer side effects than corticosteroids. However, these are not the first choice treatments.
Antifungals
They are used in the form of gels, creams or shampoos, alternating with other drugs. They can be used at 1 or 2% like ketoconazole, depending on the intensity and the area to be treated.
In the most severe cases, oral treatments with tetracyclines can be used, which decrease sebaceous secretion. In general, the response to treatment for seborrheic dermatitis is good.
You should be aware, however, that maintenance therapy will be necessary as the disease persists for months or years. You will have flare-ups that will improve during the warmer seasons. They will get worse in cold months and in situations of fatigue and emotional stress.